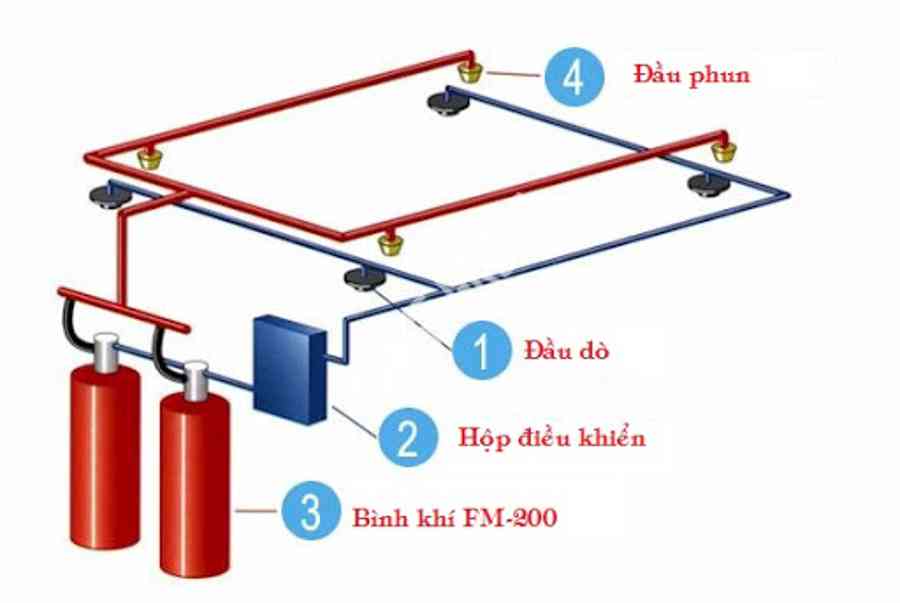
| Short name
|
Long name
|
Standards under development
|
Other notes
|
| Auto-ID Labs |
Auto Identification Center |
Networked RFID (radiofrequency identification) and emerging sensing technologies |
|
| Connected Home over IP |
Project Connected Home over IP |
Connected Home over IP (or Project Connected Home over IP) is an open-sourced, royalty-free home automation connectivity standard project which features compatibility among different smart home and Internet of things (IoT) products and software |
The Connected Home over IP project group was launched and introduced by Amazon, Apple, Google,[182] Comcast and the Zigbee Alliance on December 18, 2019.[183] The project is backed by big companies and by being based on proven Internet design principles and protocols it aims to unify the currently fragmented systems.[184]
|
| EPCglobal |
Electronic Product code Technology |
Standards for adoption of EPC (Electronic Product Code) technology |
|
| FDA |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
UDI (Unique Device Identification) system for distinct identifiers for medical devices |
|
| GS1 |
Global Standards One |
Standards for UIDs (“unique” identifiers) and RFID of fast-moving consumer goods (consumer packaged goods), health care supplies, and other things
The GS1 digital link standard,[185] first released in August 2018, allows the use QR Codes, GS1 Datamatrix, RFID and NFC to enable various types of business-to-business, as well as business-to-consumers interactions.
|
Parent organization comprises member organizations such as GS1 US
|
| IEEE |
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
Underlying communication technology standards such as IEEE 802.15.4, IEEE P1451-99[186] (IoT Harmonization), and IEEE P1931.1 (ROOF Computing). |
|
| IETF |
Internet Engineering Task Force |
Standards that comprise TCP/IP (the Internet protocol suite) |
|
| MTConnect Institute |
— |
MTConnect is a manufacturing industry standard for data exchange with machine tools and related industrial equipment. It is important to the IIoT subset of the IoT. |
|
| O-DF |
Open Data Format |
O-DF is a standard published by the Internet of Things Work Group of The Open Group in 2014, which specifies a generic information model structure that is meant to be applicable for describing any “Thing”, as well as for publishing, updating and querying information when used together with O-MI (Open Messaging Interface). |
|
| O-MI |
Open Messaging Interface |
O-MI is a standard published by the Internet of Things Work Group of The Open Group in 2014, which specifies a limited set of key operations needed in IoT systems, notably different kinds of subscription mechanisms based on the Observer pattern. |
|
| OCF |
Open Connectivity Foundation |
Standards for simple devices using CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) |
OCF (Open Connectivity Foundation) supersedes OIC (Open Interconnect Consortium)
|
| OMA
|
Open Mobile Alliance
|
OMA DM and OMA LWM2M for IoT device management, as well as GotAPI, which provides a secure framework for IoT applications
|
|
| XSF |
XMPP Standards Foundation |
Protocol extensions of XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol), the open standard of instant messaging |
|
| W3C
|
World Wide Web Consortium
|
Standards for bringing interoperability between different IoT protocols and platforms such as Thing Description, Discovery, Scripting API and Architecture that explains how they work together.
|
Homepage of the Web of Things activity at the W3C at https://www.w3.org/WoT/
|